Origins of Oil and Gas Theories
I’m interested in organic theory. When it became clear that petroleum deposits could be found all over the world, early hypotheses proposed an inorganic origin. Metallic carbides deep below the Earth interacted with water at high temperatures to generate acetylene (C H), which then condensed to make heavier hydrocarbons, according to Dmitri Mendeleyev (1877), a Russian scientist and the father of the periodic table of elements. This reaction can be easily duplicated in the laboratory.
laboratory. Sokoloff (1890) offered a cosmic origin as an alternative inorganic explanation. His notion was that hydrocarbons were discharged from the earth’s innards onto surface rocks as rain from the first nebular materials from which the solar system was born. This idea, as well as others, are called extraterrestrial theory
Two discoveries in the twentieth century sparked a revived interest in the inorganic mode of creation among others: the existence of carbonaceous chondrites (meteorites) and the revelation that several celestial planets have atmospheres including methane, such as Saturn, Titan, and Jupiter. Inorganic processes are the sole known source of methane.
It has been proposed that the earth’s original atmosphere contained methane, ammonia, hydrogen, and water vapor; add photochemical reactions (due to UV radiation) and the result is the formation of an oily, waxy surface layer that could have been home to a variety of developing pre-biotic compounds, including life’s precursors.
The inorganic hypothesis, on the other hand, has flaws. To begin with, there is no concrete evidence to establish whether the organic material in chondritic meteorites came from a biologically generated parent material or came from an inorganic source. Other heavenly bodies follow a similar logic.
Second, there is no field evidence that inorganic processes have occurred in nature, despite mounting evidence for an organic origin, and third, if an inorganic origin is a primary methodology for the creation of hydrocarbons, large amounts of hydrocarbons should be emitted from volcanoes, congealed magma, and other igneous rocks,
Conclusion: There are undeniable examples of indigenous magmatic oil, but they are uncommon, and the amounts of stored oil (pools) are insignificant. Other aspects to consider, Commercial accumulations are limited to sedimentary basins and petroleum seeps, whereas igneous and metamorphic rocks are devoid of accumulations. The organic matter in shales may be compared to that in the nearby pool using gas chromatography. As a result, contemporary thought argues that most petroleum is formed by the thermal maturation of organic materials and that the huge reservoirs (pools) of oil and gas were created from an Organic Origin.
Organic Development Theory: There are several persuasive arguments in favor of an organic development hypothesis. The carbon-hydrogen-organic matter link is first and foremost.
Organic stuff, both plant and animal, is made up mostly of carbon and hydrogen. Furthermore, the living activities of plants and animals create carbon, hydrogen, and hydrocarbons on a continuous basis. It was revealed that there was a huge breakthrough when it was discovered that, Many living creatures produce hydrocarbons and similar chemicals, which are deposited in sediments with little or no modification.
The chemical properties of petroleum reserves were the subject of the second set of observations. Nitrogen and porphyrins (plant-derived chlorophyll, animal-derived blood derivatives) are contained in all organic stuff, as well as several petroleums. Because porphyrins are quickly oxidized and decomposed under certain conditions, the presence of porphyrins implies that conditions existed early in the creation process. Furthermore, a low oxygen level indicates a decreasing atmosphere.
As a result, there’s a good chance that petroleum was formed in an anaerobic and reducing environment.
The third set of observations focused on physical traits. Almost all petroleum is found in sediments that are mostly marine in origin.
Petroleum in non-marine sediments is most likely transported into these locations from adjacent marine source materials.
Furthermore, temperatures in underground petroleum reserves seldom surpass 300 degrees Fahrenheit (141 oC). Temperatures in the presence of porphyrins, however, never surpassed 392oF (200oC) since they are destroyed at this degree. As a result, petroleum formation is most likely due to a low-temperature event.
Finally, based on more recent oil findings in sediments, time needs may be less than 1MM years.
However, physical circumstances on Earth may have been different in the geologic past, and developing liquid petroleum may have taken far longer.
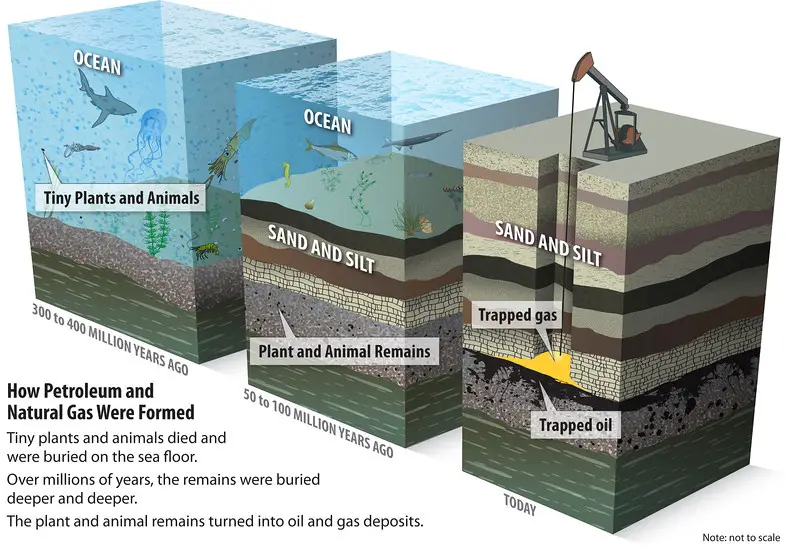
Summary of the Organic Hypothesis As the oil and gas industry matured and geologists looked for fresh resources around the turn of the century, the organic theory became the accepted view. Simply put, the organic theory maintains that the carbon and hydrogen required for the production of oil and gas came from early marine life forms, especially marine plankton, that lived on the Earth throughout the geologic past. Plankton makes up nearly all of the living stuff in the ocean, accounting for roughly 95 percent of all living matter. All living organisms, including plankton and other types of marine life, get their energy from the Sun. The relics of these early living forms were caught by erosion and sedimentation when they perished. Layers upon layers of organic-rich muck and silt covered prior layers of organic-rich sediments, resulting in strata on the sea bottom rich in previous life’s fossil remnants. Organic matter was progressively transformed into oil and gas through thermal maturation processes (decay, heat, pressure).
After a long period of geologic time (millions of years), the organic-rich sediments were transformed into rock strata. More geologic time passed, and the strata were deformed, buckled, shattered, and raised; liquid petroleum flowed upward through porous rock until it got trapped and could no longer flow, generating the oil and gas that we currently seek for. However, the chemistry of the hydrocarbons present in the final product (oil, gas) differs from that of living creatures. . Between the deposition of organic remnants and the synthesis of the ultimate product, transformation occurs. Petroleum End Product = ([Raw Material + Accumulation + Transformation + Migration] + Geologic Time) is the basic formula for the production of petroleum (oil, gas).
The Source of Oil and the Rate at Which It Is Produced
The production of crude oils takes just a short time when adequate organic materials are in about 2–5 days, reservoir rocks can be found offshore.
Because porphyrins are also found in animal blood, it’s probable that some crude oils came from the animals that were also buried and petrified in numerous sedimentary rock strata. Indeed, at a commercial thermal conversion process facility, animal slaughterhouse wastes are now routinely turned into high-quality oil and high-calcium powdered and strong liquid fertilizers in under two hours.
used. Plant material, such as diatoms (single-celled marine and freshwater photosynthetic organisms)12 and coal beds, are thought to be the primary source of crude oil by most petroleum geologists (huge fossilized masses of plant debris). 13 Because coal beds are found in the same sedimentary geological strata as petroleum reservoir rocks, the latter is thought to be the source of most Australian crude oils and natural gas. 14 For example, it has been proved in the laboratory that mild heating of brown coals from Victoria’s Gippsland Basin, to replicate their quick deeper burial, produces crude oil and natural gas similar to that found in the Gippsland Basin.
What is the significance of oil and gas? Oil is the lifeblood of developed countries. Since the mid-1950s, oil has been the world’s most important source of energy. Its products are essential to contemporary life, providing energy to the power industry, heat homes, and fuel for automobiles and planes that transport goods and people throughout the world.
What is the significance of the oil and gas industry? The oil and gas sector sustains millions of employment in the World, lowers consumer energy bills, and maintains national energy security. Oil, natural gas, and coal account for 80% of all energy in the United States.
What is the significance of gas? It produces heat for cooking and heating, as well as supplying energy to homes and businesses through power plants. It also powers a variety of industrial activities that generate materials.
It may be found in everything from glass to clothes, and it’s a key element in paints and plastics.
What is the significance of having oil? Gasoline accounts for roughly half of all petroleum use in the United States. The distillate is made from oil and is used to make diesel fuel for vehicles, trains, boats, and barges, as well as heating oil for households. As a result, the United States continues to rely on petroleum imports to satisfy its energy requirements.
What is the significance of oil and gas? – Related Concerns
What are the advantages of utilizing gas versus oil?
Natural gas is more ecologically friendly than other fossil fuels since it burns cleaner. When compared to other fossil fuels, it is safer and easier to store. Unlike electric electricity, natural gas is incredibly dependable.
During a storm, this might be knocked out. Other fossil fuels are more costly than natural gas.
What makes oil the most valuable resource?
Oil is the lifeblood of developed countries. Since the mid-1950s, oil has been the world’s most important source of energy. Its products are essential to contemporary life, providing energy to the power industry, heat homes, and fuel for automobiles and planes that transport goods and people throughout the world.
What is natural gas?
Natural gas is a fossil fuel that was created deep under the surface of the planet. Natural gas is made up of a variety of chemicals. Natural gas also comprises nonhydrocarbon gases including carbon dioxide and water vapor, as well as natural gas liquids (NGLs), which are also hydrocarbon gas liquids.

Is there still a need for oil?
If we don’t need food, medicine, or transportation fuel by 2050, we won’t need oil. There’s also the issue of being unable to cultivate food on a solar or wind farm. Petroleum is utilized for more than just fuel; it’s also used to make medications, heart valves, and other medical devices.
Why is oil harmful to your health?
Saturated fats (mainly animal and coconut oil), monounsaturated fats (olive oil), and polyunsaturated fats (omega-3 and -6 oils) are all linked to the development of new atherosclerotic lesions. Oils of all sorts, including olive oil, have been linked to arterial damage and the advancement of heart disease.
What are the dangers of oil and gas?

Pollution has a negative influence on communities.
Furthermore, when fossil fuels are consumed by vehicles, the environment suffers. They release considerably more contaminants from power plants and industrial operations. Fossil fuel development can potentially cause cancer, birth deformities, and liver damage by leaking hazardous compounds into the land and drinking water supplies.
What are the similarities and differences between natural gas and oil?
Crude oil and natural gas are both fossil fuels generated over thousands of years from the remnants of deceased animals and plants. They are both utilized as heat sources, create energy, and are made up of various hydrocarbons, which are hydrogen and carbon molecules.
What proportion of oil is utilized as a source of energy?
An average barrel of crude oil gets processed into gasoline to the tune of 45 percent. The remaining 29% is processed into diesel fuel. The last of the oil is a chemical that is used to produce plastics and other things (see image Products made from a barrel of crude oil, 2016).
What is the most precious commodity on the planet?
Data is presently considered the world’s most valuable and vulnerable resource, with a total market value of $280 billion predicted for the cyber world by 2025.
What is the most precious resource on the planet?
Data is the most precious (and fragile) resource on the planet.
How do people utilize oil in their everyday lives?
Oil and natural gas may be found in common items like lipstick and deodorant, as well as life-saving medical instruments like MRI scanners and pacemakers. Plastics, lubricants, waxes, tars, and even asphalt for our roadways are all made from byproducts of oil refining.
What type of fossil fuel is the dirtiest to burn?
Coal is the dirtiest of the fossil fuels, accounting for approximately 0.3°C of the 1°C rise in world average temperatures, making it the single most significant contributor to global warming. When oil is burnt, it emits a tremendous quantity of carbon — almost a third of the world’s total carbon emissions.
What is the most significant drawback of natural gas?
Carbon Dioxide Emissions from Natural Gas: Natural gas has a number of drawbacks, one of which is that it emits carbon dioxide, which is harmful to our environment. Climate change and global warming will result from the continued injection of carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
What is it about natural gas that is so bad?
Is it true that natural gas is harmful to the environment? While carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, Although the quantity of emissions produced by burning natural gas is low, it does emit methane, a powerful greenhouse gas that seeps into the atmosphere in large quantities. Carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides (NOx), and sulfur dioxide are all released when natural gas is burned (SO2).
What are the ten gas examples?
Helium, Argon, Neon, Krypton, Radon, Xenon, Nitrogen, Hydrogen, Chlorine, Fluorine, and Oxygen are among the 11 gases. Because they are all elements, they are referred to be pure gases. These names may be used as a superb illustration of a gas matter.
What are the four characteristics of gas?
Characteristics physical
Because most gases are difficult to perceive directly, they are defined using four physical attributes or macroscopic characteristics: pressure, volume, particle number (chemists classify particles by moles), and temperature.
In the residence, what kind of gas is used?
When it comes to the sort of gas used in residences, gas bottles are virtually usually filled with LPG. Propane, butane, or a combination of the two is the kind of gas utilized in dwellings. Natural gas (mains gas) or compressed natural gas (CNG), both of which are methane, are the two types of gas utilized in houses.
What is the meaning of the term “natural gas”?
As you can see, the entire process is perfectly natural and results in the development of a colorless, odorless, extremely combustible gas. In some ways, the term “natural gas” is self-explanatory. Biogenic gas, on the other hand, has around 20% to 30% less methane than is found in natural gas.
Conclusion
All known data suggests a recent catastrophic genesis from plant and other organic debris for the world’s massive oil reservoirs, which is compatible with the biblical narrative of earth’s history. In the pre-Flood world, vast forests grew on land and water surfaces17, and the waters were teeming with diatoms and other microscopic photosynthetic creatures. The woods were uprooted and carried away during the worldwide Flood calamity. Huge amounts of plant detritus were quickly buried in what became coal beds, and organic matter was spread throughout the various layers of sedimentary rock that were produced in a catastrophic manner. As the Flood continued, the coal beds and fossiliferous sediment strata became deeply submerged. As a result, their temperatures rose to the point where crude oils and natural gas could be produced quickly. These traveled until they became trapped in reservoir rocks and structures, eventually becoming today’s oil and gas reserves.